What is ‘anaesthesia’?
Anaesthesia is the word we use to describe how we prevent you feeling pain during surgery.
Stops you feeling pain and other feelings | |
|---|---|
It can be given in many ways.
Not all anaesthesia puts you to sleep
It can work on different parts of the body |
What are the different types of anaesthesia
Local anaesthesia

A local anaesthetic numbs a small part of your body. You are awake but do not feel pain.
Regional anaesthesia
A regional anaesthetic numbs a large part of your body such as your arm or your leg.
It is given near to the area where you will have your operation.
You are awake but do not feel pain.
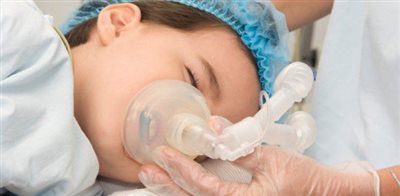
General anaesthesia
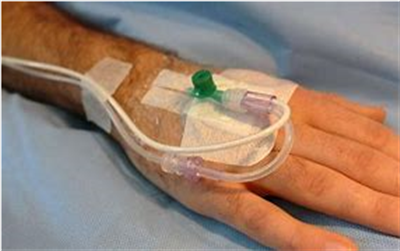
If you have a general anaesthetic you will be asleep and will not feel pain. Anaesthetic drugs can be injected into a vein.
Anaesthetic gases can be breathed into the lungs. As the anaesthetic drugs wear off you wake up.
You may get more than one type of anaesthetic to keep you comfortable.
You may also be given drugs to help you relax. This is called sedation.
The Anaesthesiologist

Anaesthesiologists are doctors who are experts in the treatment of pain and in the care of very ill patients.
You will be treated by a consultant anaesthesiologist, or by an anaesthesiologist in training.

There is always a consultant available to help if needed.
What does your anaesthesiologist do?

We keep you safe during your surgery.

We make a plan with you for your anaesthetic.

We give you your anaesthetic.

We plan your pain control with you.

We manage your care in the Intensive Care Unit if needed.
Before you come into hospital

How to prepare for your operation

You should try to quit smoking as long before your surgery as you can. Smoking increases the risk of breathing problems during and after an operation. If you cannot stop smoking completely, smoking fewer cigarettes than usual will help.
If you are very overweight, reducing your weight will help to reduce your risk of problems with your anaesthetic.
Visit your dentist for treatment if you have loose or broken teeth or crowns that are not secure.
If your teeth are not secure, they may be damaged.
If you have a long-term medical problem such as

Diabetes

Asthma
Bronchitis
Thyroid problems

Heart problems
High blood pressure

Please ask your GP if you need a check-up.
Pills, medicines, herbal remedies and allergies

Please bring a written list of every medication and herbal remedy you are taking. Include prescription items and over the counter items.

If you have any allergies, a note of these will also be helpful.
Choice Of Anaesthetic

Your anaesthesiologist will discuss with you which anaesthetic methods can be used.
The type of anaesthetic depends on:
Your operation

Your answers to the questions you have been asked

Your physical condition

Your preferences and the reasons for them

Your anaesthesiologist’s recommendations for you and the reasons for them

The equipment, staff and other resources at your hospital.

You will meet your anaesthesiologist before your operation, either on the ward the night before or in theatre before your surgery. You may also have been assessed by the Perioperative Assessment Clinic.

Your anaesthesiologist will look at the results of your health check and may ask you more questions about your health.
He or she may also need to listen to your chest with a stethoscope
They may need to examine your neck and jaw movements, and look in your mouth.
Further Information